
PPWR 2025: Everything you need to know about the new EU Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation
What companies need to know about the PPWR
To address the challenges of climate change and environmental pollution, the EU Commission has introduced the Green Deal. Its goal is to achieve ecological transformation and climate neutrality across all 27 EU member states by 2050. Therefor various initiatives have been introduced including the Circular Economy Action Plan, which aims to accelerate the transition to a resource-efficient circular economy.
A key element is the new EU Packaging & Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR). This regulation presents both challenges and opportunities for business and consumers.
Here you will find the most important facts and requirements of the PPWR. Find out how BellandVision can help your company get ready for the new legislation and the implementation of the PPWR.

What is the EU packaging regulation PPWR?
The Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) is an EU regulation governing the handling of packaging and packaging waste within the European Union.
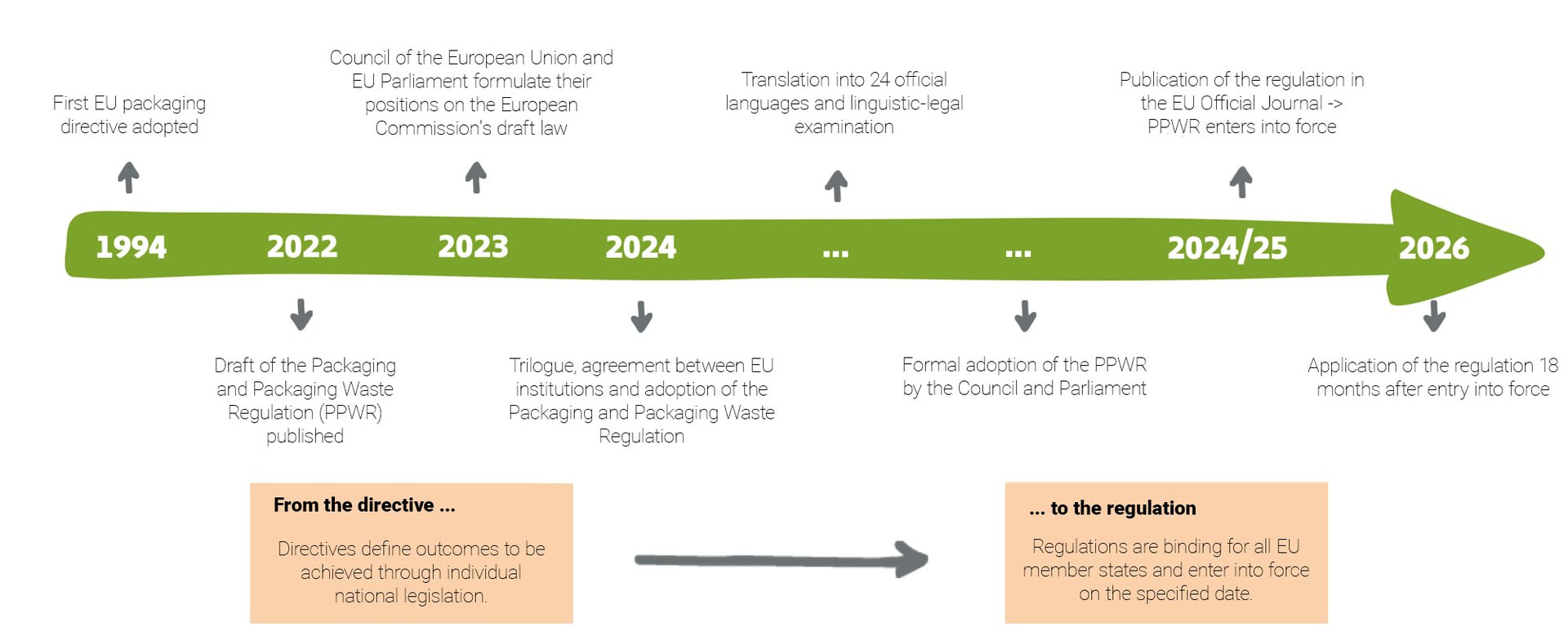
Milestones of the PPWR:
▶ Draft: End of 2022, the EU Commission published the first draft of the PPWR.
▶ Approval: By April 2024, both the EU Parliament and the Council of the European Union voted in favor of the regulation as part of the trilogue procedure.
▶ Translation and review: Translation into all 24 official EU languages and legal language review.
▶ Approval: The Committee on the Environment, Public Health and Food Safety, the EU Parliament and the Council of the European Union had to approve the reviewed versions.
▶ Entry into force: The regulation comes into force 20 days after publication in the Official Journal of the European Union.
▶ Legal enforcement: The PPWR will become legally binding 18 months after it enters into force, likely in 2026.
The PPWR regulates the handling of packaging and packaging waste sold in the European Union introducing new requirements for packaging design, the use of recyclates in plastic packaging, and specifications for reusable systems. A significant difference to previous EU legislation is that the PPWR, unlike its predecessor, the EU Packaging Directive 94/62/EC, is a regulation and not a directive.
So the PPWR is directly applicable in all EU member states. This ensures uniform implementation across the EU. National regulations are only superseded by directly applicable EU law to the extent and for as long as they contradict the content of EU law in a specific case and an interpretation of national law in line with EU law is not possible (socalled primacy of application of EU law). National regulations that do not contradict the Regulation remain valid. In addition, some articles of the PPWR contain socalled “opening clauses” that explicitly permit special national regulations.
How does the PPWR promote environmental protection?
The EU packaging regulation (PPWR) brings numerous ecological benefits for environmental protection. It not only contributes to achieving climate targets, but also to sustainable development in the European Union:
-
Supporting climate goals: The PPWR promotes the achievement of EU climate protection targets such as climate neutrality by 2050 and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Careful use of resources: By improving the use of raw materials, the PPWR contributes to an accelerated transition to an ecologically sustainable circular economy.
-
Standardized EU regulations: The PPWR applies directly in all EU member states, ensuring consistent requirements.
-
Promotion of recycling: The PPWR improves the recyclability of packaging and the market for secondary raw materials.
-
Waste prevention and reuse: The regulation aims to reduce packaging waste or prevent it from being generated in the first place due to reuse.
When will the PPWR be implemented?
The European Commission published the first draft of the EU Packaging Regulation (PPWR) in November 2022. The Council of the European Union and the European Parliament took a position followed by trilogue negotiations at the beginning of 2024. After initial approval by the European institutions and adoption of the English version by the EU Council and EU Parliament end of April 2024, the PPWR was translated into the 24 official EU languages and subjected to linguistic and legal review.
After the EU Parliament has approved the language-legal checked versions, the Council of the European Union plans to review the version of the PPWR already adopted by the EU Parliament on Monday, December 17, 2024. If the regulation receives the final approval of the Council, it can be published in the Official Journal of the European Union and will enter into force 20 days after publication. The PPWR will not apply in the EU member states until 18 months after it enters into force.
What requirements do result from the PPWR for companies?
The new EU packaging regulation introduces significant changes for manufacturers.
Key obligations at a glance:
-
Conformity: Manufacturers must ensure that their packaging is designed, manufactured and labeled in accordance with the requirements of the PPWR. For each type of packaging, a socalled “conformity assessment procedure” must be carried out, technical documentation drawn up and an EU declaration of conformity issued.
-
Circular design: The PPWR defines criteria for recyclable packaging. Manufacturers and retailers in the EU must design packaging that is recyclable at the end of its life cycle. From 2030, only products whose packaging is recyclable may be sold on the European market.
-
Minimum recycled content quotas: The regulation stipulates a minimum proportion of recycled materials in certain plastic packaging. Retailers are obliged to only use packaging that meets these quotas.
-
Packaging reduction: The PPWR sets specific targets for minimizing packaging waste. Retailers must actively take measures to reduce the waste from their packaging. In addition, stricter requirements are introduced for packaging functions, weight, empty space and size.
-
Labeling requirements: The regulation defines requirements for the labeling and provision of information for packaging. The labels with information on material composition are intended to make it easier for consumers to separate waste.
-
Compostability: The regulation places a stronger focus on bio-based raw materials and compostable packaging. While the use of bio-based plastics will initially be evaluated by the EU Commission, the EU regulation stipulates that certain packaging must be compostable in future.
-
Reusability: The PPWR sets clear criteria for the reusability of packaging. Producers must prove compliance with these criteria as part of the conformity assessment procedure.
How will the PPWR be implemented?
The implementation and detailing of many requirements is to be carried out retrospectively through numerous delegated and implementing acts. These serve as technical requirement for the effective implementation of the PPWR, but at the same time create uncertainties for the respective stakeholders. Precise requirements - as illustrated here using the example of Article 6 (recyclable packaging) - are in some cases not yet fully defined on the day of entry into force.

Steps towards compliance with the EU Packaging Regulation 2025

Time is crucial, as both the recyclable design of packaging and the use of recyclate require significant time. Before packaging can be converted, thousands of items in a manufacturer's product range often have to be evaluated to determine the need for action.
BellandVision offers flexible software solutions and lean processes to determine the status quo quickly and precisely. The focus is on individual customer requirements and advice. Our partner Circpack by Veolia supports us for example with operational sorting tests in our own facilities or the certification of recyclable packaging - all from a single source.
BellandVision customers can also benefit from the use of recyclate. With Veolia, Europe's largest recycler of plastic packaging, as its affiliated company, BellandVision can support customers in the procurement of recyclate. In BellandVision, manufacturers of packaging subject to system participation have a reliable partner who not only provides them with optimal support for system participation, but also for future challenges.
“Our Circular Consultants have already analyzed over 30,000 packages and have been advising manufacturers and retailers on recyclingfriendly packaging design for years. This expertise and our global recycling network make us the top address for Design4Recycling solutions. This close cooperation and continuous exchange of knowledge enables us to achieve the ambitious recycling targets and recycling specifications,” explains BellandVision Managing Director Diana Uschkoreit.
Frequently asked questions about the EU packaging regulation PPWR
Why do we need a PPWR?
The Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) is a central component of the EU Green Deal to achieve climate neutrality by 2050. It is the urgent response to current environmental problems. It addresses the packaging sector, which plays a key role in the sustainable circular economy.
Reasons for the PPWR:
-
The previous directive from 1994 did not have the desired effect. 18 out of 27 EU Member States failed to meet the recycling targets.
-
The regulation creates uniform standards for the packaging sector throughout the EU. The PPWR is directly applicable in all EU countries. This ensures uniform application and replaces conflicting national regulations.
-
The PPWR encourages the careful use of resources and the use of secondary raw materials.
-
By improving packaging standards, the regulation helps to reduce CO2 emissions. It is an important factor in the EU Circular Economy Action Plan.
The PPWR will contribute to environmental protection and sustainable development in the EU.
What exactly is the PPWR?
The Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) is a regulation issued by the EU. It aims to reduce the environmental impact of packaging by promoting recycling, the use of recyclate - i.e. sustainable materials - reuse and the reduction of packaging waste.
How does the PPWR differ from the previous Packaging Directive?
The PPWR (Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation) differs in several essential points from the earlier Packaging Directive:
-
Legal form: as a regulation, the PPWR applies directly in all EU member states without the need for transposition into national law. The previous directive contained targets and first had to be transferred into national law.
-
Entry into force: The PPWR enters into force simultaneously in all EU countries and replaces conflicting national regulations, ensuring more uniform application throughout the EU.
-
Binding force: The regulation is binding in all its parts. Through its uniform application in all member states, the PPWR promotes greater harmonization of EU packaging regulations.
The PPWR is intended to improve the effectiveness and enforceability of EU packaging regulations and ensure more consistent implementation in all Member States.
What are the main objectives of the PPWR?
The PPWR (Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation) pursues several key objectives to improve sustainability in the packaging sector
-
Climate neutrality: it supports EU climate neutrality targets by 2050 and promotes resource efficiency through the transition to a circular economy.
-
Uniform standards: As a regulation valid in all EU member states, it creates uniform standards and improves the implementation of recycling targets.
-
Recycling: The PPWR optimizes the recyclability of packaging, strengthens the market for secondary raw materials and aims to reduce packaging waste.
Who is affected by the PPWR?
The regulation affects all companies that make packaging or packaged products available on the Union market.
How does the PPWR affect my business?
Companies may need to check the compliance of their packaging, document it and, if necessary, adapt their packaging in order to
-
Improve recyclability
-
Use recyclate in plastic packaging
-
make the packaging compostable
-
Reduce packaging to a minimum
-
comply with labeling requirements
You may also need to
-
introduce systems for the return and reuse of packaging (reusable) and
-
restrict the use of certain materials.
BellandVision offers specific advice and supports to ensure compliance.
When does my company have to comply with the requirements of the PPWR?
The PPWR sets staggered deadlines for the implementation of various requirements. Some depend on delegated and implementing acts that have yet to be drawn up and will follow after the regulation comes into force.
The new requirements on minimum recycled content rates and the recyclability of packaging are particularly important. Although the exact deadlines are not yet 100% certain, it is advisable to start preparations early. This will enable your company to implement all the necessary adjustments in time and proactively tackle potential challenges.
How can companies prepare for the PPWR?
To prepare for the PPWR, companies should take several steps:
-
Packaging portfolio analysis: first, a thorough review of the current packaging portfolio is required.
-
Development of packaging solutions: Based on this, it is important to develop recyclable packaging solutions and drive procurement, planning and the use of recycled plastics.
-
Adjustments and training: At the same time, production processes need to be adapted and employees trained to meet the new requirements.
BellandVision offers comprehensive support with compliance and advice on packaging issues. This provides companies with the necessary expertise to understand and effectively implement the requirements of the PPWR.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with the PPWR?
The PPWR provides various consequences for non-compliance with its requirements. Packaging that does not comply with the PPWR requirements may no longer be placed on the market within the EU.
-
Fines: Violations may result in financial penalties in the form of fines (the exact amount and structure are still under discussion)
-
Market exclusion: Companies must also expect economic consequences such as loss of sales if their products have to be withdrawn from the market due to non-compliant packaging. Non-compliance can lead to considerable reputational damage.
-
Legal action: In addition to administrative penalties, there could also be the threat of further legal sanctions in serious cases.
The detailed penalties and their implementation are still being worked out and may vary from Member State to Member State.
What impact does the PPWR have on small businesses?
The new EU packaging regulation provides simplifications for small businesses that work with different types of packaging.
Including
-
transport packaging,
-
reusable packaging,
-
primary production packaging and
-
service packaging at the point of sale.
The aim is to keep the administrative workload for these companies as low as possible.
The specific details of these relief measures have not yet been specified. Small businesses should closely follow further developments and clarifications of the regulation in order to benefit from possible relief measures.